ServerlessLLM: Locality-Enhanced Serverless Inference for Large Language Models paper repo
What are the motivations for this work?
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently been incorporated into various online applications, and Serving LLM inference at scale is a challenging problem. LLM requires huge GPU resources, which is expensive today.
The technical challenge of serving LLM includes:
- LLM is a memory intensive application
- highly dynamic, bursty traffic for LLM application
The technical challenge of serving LLM as Microservices includes:
- Transport from model repositories
- Costly checkpoint loading from storage devices
The current solution for Machine Learning Serverless Application include checkpointing, which has significant overheads and latencies. And there are other solutions (and drawbacks) for Regular Serverless Application:
- Keep instances warm: waste GPU resources
- Memory Caching: not efficient for Large Models
- Additional Storage Server: Large communication overhead
What is the proposed solution?
Leveraging the multi-tier storage architecture for local checkpoint storage and utilizing their significant storage bandwidth for efficient checkpoint loading, which includes:
- Fast LLM checkpoint loading: Increase memory addressing efficiency
- Locality-driven LLM inference with live migration
- Locality-aware server allocation
Fast LLM checkpoint loading
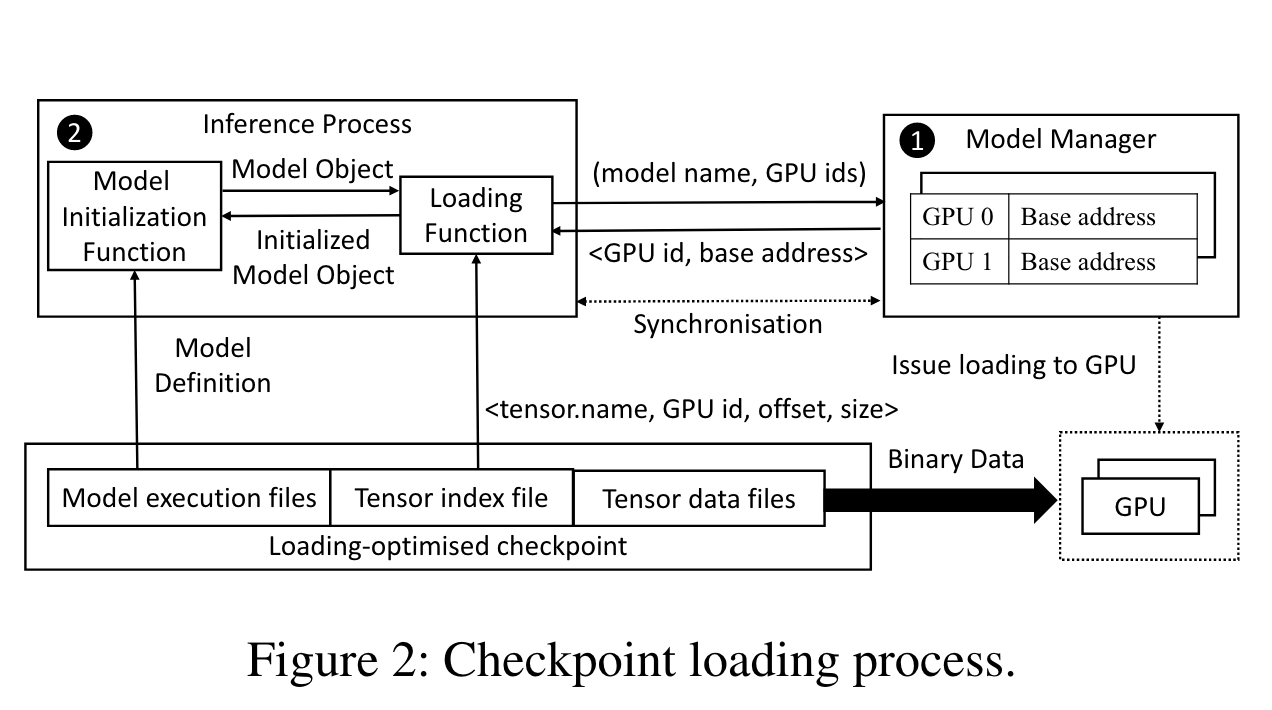
- Preloading on GPU
- Utilize parallelized PCIE, direct r/w and throughput optimization.
- Question Mark: Preloading may introduce new overheads, and description here is not clear enough.
Locality-Driven LLM Inference with Live Migration
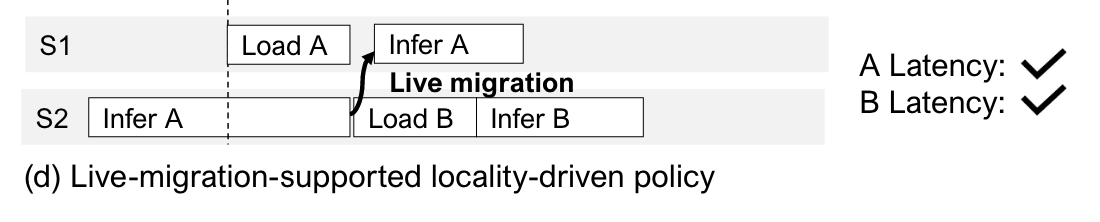
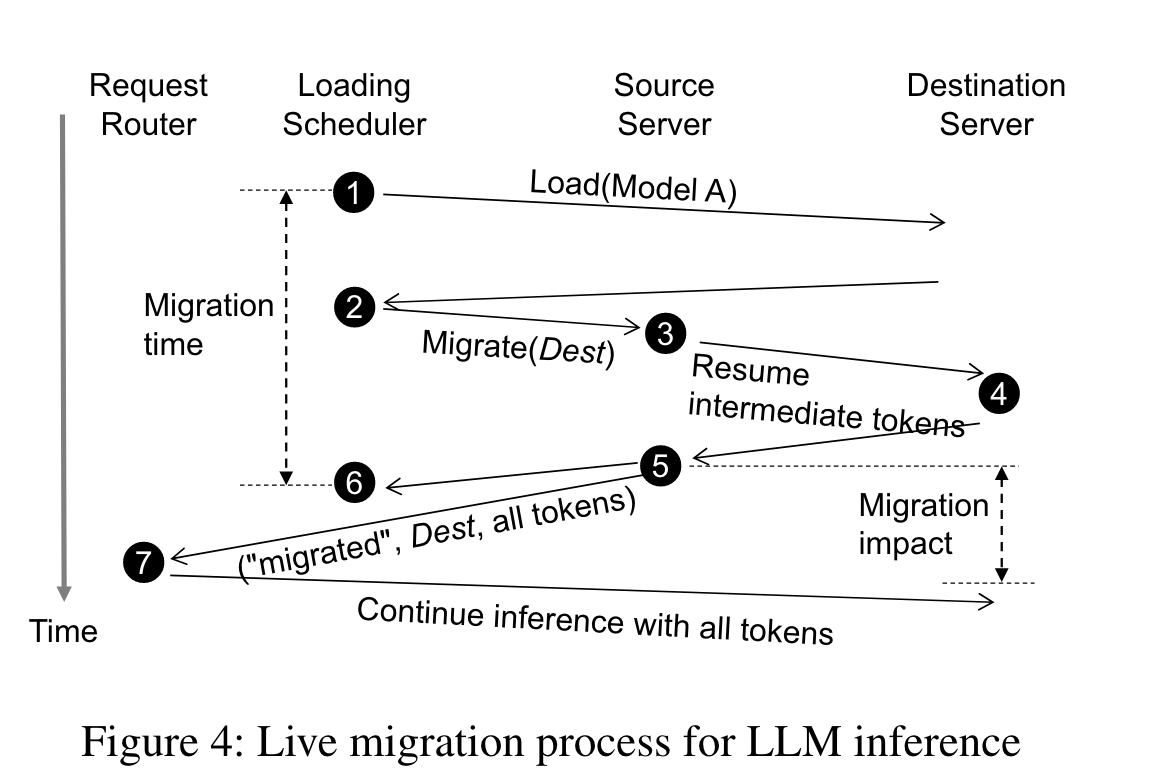
- token-based migration
- And fault tolerance
- The model loading scheduler sends a model loading request to dest server to load model A into GPUs. If there is an idle instance of model A on dest server, the scheduler skips this step.
- After loading, the scheduler sends a migration request carrying the address of dest server to src server.
- Upon receiving a migrate request, src server sets itself as “migrating”, sends a resume request with intermediate tokens (i.e., input tokens and the output tokens produced before step 3) to dest server if the inference is not completed. Otherwise, it immediately returns to the scheduler.
- dest server recomputes KV cache given the tokens in the resume request.
- Once resume request is done, src server stops inference,returns to the scheduler, and replies to the request router with all tokens (i.e., the intermediate tokens together with the remaining tokens produced between step 3 and step 5) and a flag “migrated”. If long-context, the collection of all tokens can be very large thus resuming takes a long time, during which many new tokens are predicted. In such a case, we can repeat the above two steps to further reduce the tokens to send between src and dest.
- The scheduler finishes the migration, unloads model A at src server and starts loading model B.
- The request router checks the flag in the inference response. If it is “migrated”, the request router replaces src server with dest server in its route table and sends all tokens to dest server to continue inference.
Locality-Aware Server Allocation
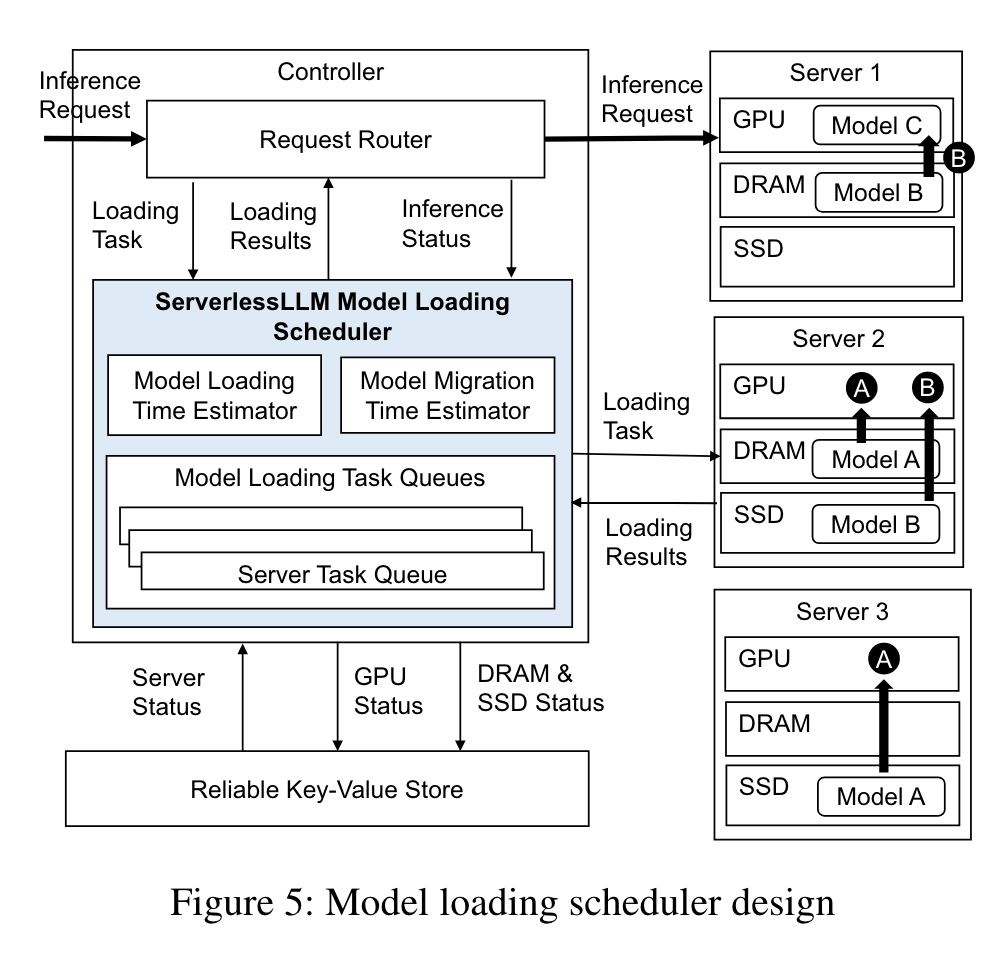 Key idea: Measure the time for migration, estimate model loading time and migration time.
Key idea: Measure the time for migration, estimate model loading time and migration time.
What is the work's evaluation of the proposed solution?
ServerlessLLM demonstrated a 10-200X improvement in latency for running OPT model inferences across datasets, which shows ServerlessLLM’s effectiveness.
- LLM workload evaluation: Described in AlpaServe
- LLM checkpoint manager: PyTorch and Safetensors
What is your analysis of the identified problem, idea and evaluation?
Running LLM on serverless might be a future trend, and the overhead brought by Serverless will amplify on LLMs. It's glad to see the solution on utilize the system throughput and add locality, however there might still have overheads and question mark exist: Recover from checkpoint, Migrating by token, Invoke by GPU address.
What are the contributions?
- LLM migration
- Measurement on LLM migration and model loading
- GPU memory management
What are future directions for this research?
WIP
What questions are you left with?
WIP
What is your take-away message from this paper?
WIP
 Canarypwn
Canarypwn